Android Debug Bridge (ADB)
The Android Debug Bridge (adb) tool, is a command line utility that allows you to interact with the device from your computer. There is a wide range of things this tool can do. We will look at some of the more common ones in this lab.
The adb tool is a client/server/daemon utility. The daemon, which is adbd, runs on the device. The server runs on your computer, and by default uses TCP port 5037. The client is also run from your computer and interacts with the server, which then communicates to the daemon on the device!
The most common uses of adb are outlined below. These will cover app installation, shell interaction, sending & receiving files, interact with packages, start activities, etc.
Enable USB Debugging
To use the adb tool, the device must have USB Debugging enabled. This only needs to be completed once on the device. This is not necessary on a Corellium virtual device.
- Open the Settings app on the device
- Scroll down to (or search for) "About phone" and select it
- Scroll down to the "Build Number"
- Tap on the Build Number until it says you are a Developer
- Go back one level in the Settings app and choose the System option
- Scroll down and tap "Developer options"
- Scroll down to the "USB Debugging" entry and toggle the button so it is enabled
ADB Usage
ADB is a command-line tool that runs on a computer and communicates with the Android device for debugging purposes. The device must have USB Debugging enabled to use ADB. ADB runs on TCP port 5037, and if it isn't already running on the computer, it will start it up on the first adb command usage.
% adb devices
* daemon not running; starting now at tcp:5037
* daemon started successfully
1C071FDF6006MB device
If you run adb devices and get "unauthorized", check the device to allow USB Debugging:
% adb devices
* daemon not running; starting now at tcp:5037
* daemon started successfully
List of devices attached
1C071FDF6006MB unauthorized
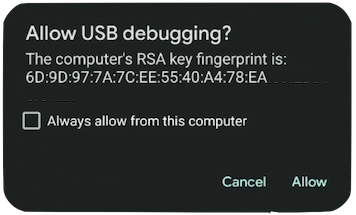
Tap on the checkbox to allow USB debugging from your computer:
Then adb devices again:
% adb devices
List of devices attached
1C071FDF6006MB device
Start & Stop ADB on Computer
Start ADB Server:
% adb start-server
* daemon not running; starting now at tcp:5037
* daemon started successfully
Stop ADB Server:
% adb kill-server
Access a Device Shell
For normal adb shell operations, you will be connected as the user shell. The "oriole" part of the prompt is the device codename.
% adb shell
oriole:/ $ whoami
shell
To become root, you can run the su command as you would on any Linux system.
% adb shell
oriole:/ $ whoami
shell
oriole:/ $ su
oriole:/ # whoami
root
App Installation and Removal
To install an application from an APK file.
% adb install InsecureShop.apk
Performing Streamed Install
Success
To uninstall an application.
First, get the package name (using the package manager command pm)
% adb shell 'pm list packages | grep -i insecureshop'
package:com.insecureshop
Then, uninstall the app
% adb uninstall com.insecureshop
Success
File Transfers
Command usage:
# Send a file from computer to device:
adb push local_filename remote_filename
# Pull a file from device to computer:
adb pull remote_filename local_filename
Examples:
% adb push file.txt /data/local/tmp
file.txt: 1 file pushed, 0 skipped. 0.1 MB/s (33 bytes in 0.000s)
% adb pull /data/local/tmp/file.txt ./file.txt
/data/local/tmp/file.txt: 1 file pulled, 0 skipped. 0.0 MB/s (33 bytes in 0.005s)